Moreover, the Sundarbans Delta is renowned for its ecological significance, acting as a natural barrier against cyclones and tidal surges, thus safeguarding the coastal communities of Bangladesh and India. Its intricate network of waterways and estuaries also supports vibrant fisheries, contributing to the livelihoods of millions of people.
Furthermore, the Sundarbans Delta holds cultural significance, with indigenous communities residing in its vicinity practising unique traditions and lifestyles deeply intertwined with the delta's ecology. As a result, the Sundarbans Delta stands as a symbol of natural wonder, resilience, and cultural heritage, captivating the imagination of people worldwide.
Are you reading in class 6,7,8,9 or 12? Creating a model of the Sundarban Delta for classes 6 to 12 can be an engaging and educational activity. Here's a simple way to make a miniature version:
Materials Needed:
1. Large shallow container (such as a baking tray or shallow plastic tub)
2. Sand or soil
3. Clay or modelling dough
4. Small plants or twigs (for mangrove trees)
5. Water
6. Small toy animals (optional)
Instructions:
1. Start by filling the shallow container with a layer of sand or soil to represent the landmass of the delta.
2. Use clay or modelling dough to create the main river channels and tributaries on the sand or soil surface.
3. Place small plants or twigs in the clay or dough to represent mangrove trees. Arrange them along the riverbanks and in low-lying areas.
4. Use your fingers or a small tool to create indentations in the clay or dough to simulate smaller water channels and estuaries.
5. Carefully pour water into the container to fill the river channels and create a wetland environment.
6. If desired, add small toy animals to represent the diverse wildlife found in the Sundarban Delta.
7. Allow the model to dry and set in place before observing and discussing the features of the Sundarban Delta.
This hands-on approach allows students to understand the geographical features and ecosystem dynamics of the Sundarban Delta tangibly and interactively.
Final Words About Sundarbans Delta
In conclusion, the Sundarban Delta emerges as a beacon of natural wonder and ecological importance, showcasing the sheer magnificence of our planet's diverse landscapes. Its breathtaking beauty, intertwined with its invaluable ecological significance, underscores the importance of safeguarding this precious treasure for future generations.
As we stand in awe of the Sundarban Delta's wonders, it becomes imperative that we take proactive steps to protect and preserve this invaluable ecosystem. Through conservation efforts, sustainable practices, and community engagement, we can ensure that the Sundarban Delta continues to thrive, serving as a sanctuary for biodiversity and a source of inspiration for all.
Let us unite in our commitment to cherish and safeguard the Sundarban Delta, recognizing it not only as a natural marvel but also as a symbol of our collective responsibility to cherish and protect our planet's ecological heritage. Together, we can ensure that the Sundarban Delta remains a source of wonder and admiration for generations to come.
12 Faqs on Sundarban Delta
Q1. What is Sundarban Delta for Class 9?
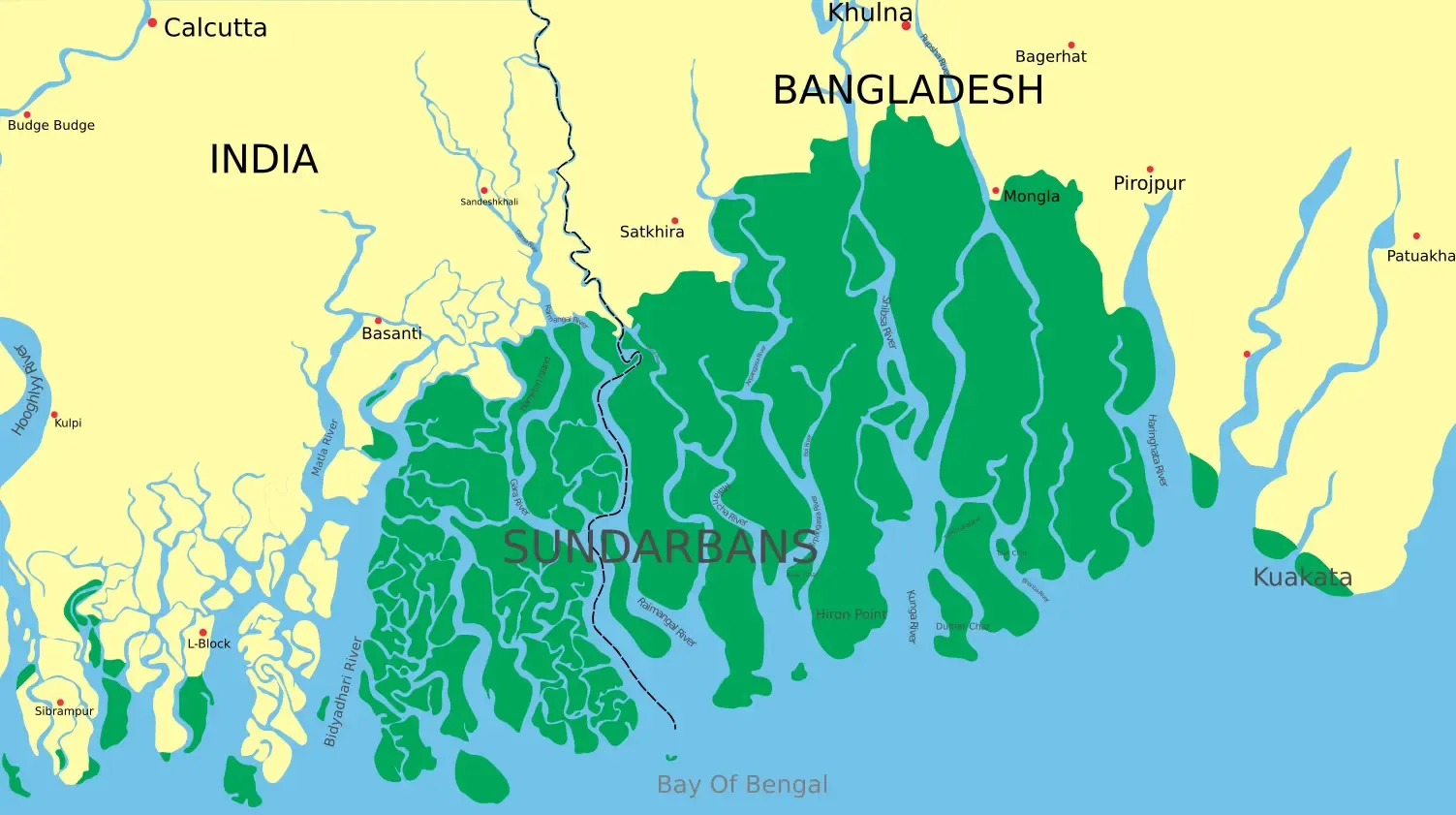
The Sundarban Delta forms through the powerful convergence of the Ganga, Brahmaputra, and Meghna rivers, earning its name from the abundant Sundari trees that thrive in its marshy terrain. Recognized as the world's largest and most rapidly expanding delta, it stands as a vital sanctuary for the majestic Royal Bengal tigers.
Q2. What is Sundarban Delta's Short Answer?
The Sundarban Delta, located at the mouth of the Ganges, Brahmaputra, and Meghna rivers, is a vast expanse of mangrove forests and waterways. It is renowned for its rich biodiversity, including the iconic Royal Bengal Tiger. As the world's largest delta, it plays a crucial role in protecting coastal areas from erosion and providing habitats for various species.
Q3. What are the features of Sundarbans delta class 9?
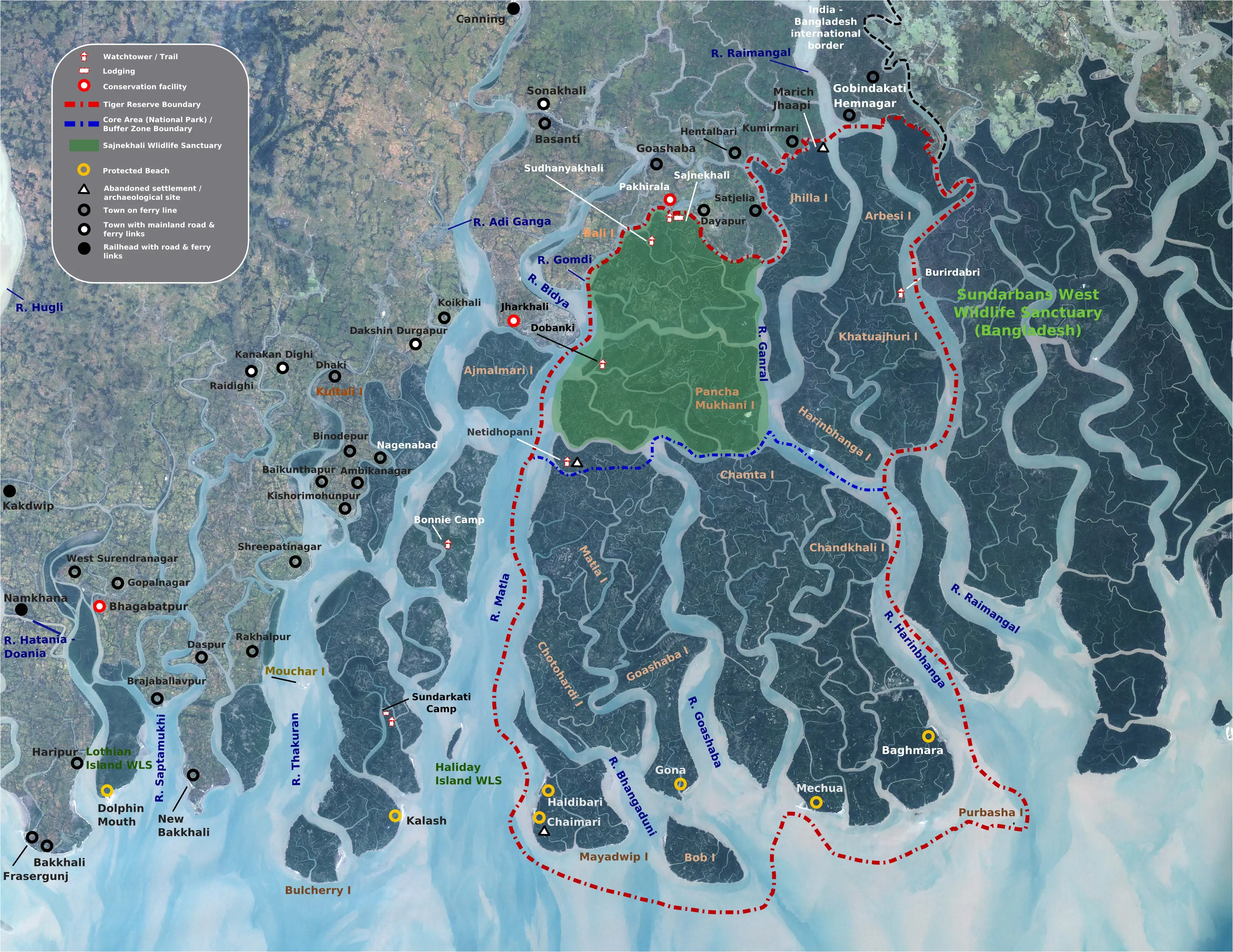
The features of the Sundarban Delta, often studied in class 9, include its extensive mangrove forests, intricate network of waterways, diverse flora and fauna, and its role as a critical habitat for endangered species such as the Royal Bengal Tiger. Additionally, the Sundarban Delta serves as a natural barrier against coastal erosion and tidal surges, protecting the region's coastal communities.
Q4. What Are the Names of the Rivers that Formed the Sundarban Delta Class 9?
The Sundarban Delta is formed by the convergence of the Ganges, Brahmaputra, and Meghna rivers, marking it as a prime example of a river delta.
Q5. How is Sundarban Delta formed class 9
The Sundarban Delta is formed through the process of sedimentation, where sediment carried by rivers like the Ganges, Brahmaputra, and Meghna is deposited in their mouths. Over time, this accumulated sediment builds up to create a vast landmass, characterized by mangrove forests, tidal creeks, and mudflats. The intricate network of waterways and estuaries in the Sundarban Delta is shaped by the constant interaction of river currents and tidal movements, resulting in its unique and dynamic landscape.
Q6. Which is the largest delta in the world Where is it located?
The largest delta in the world is the Ganges-Brahmaputra Delta, also known as the Bengal Delta. It is located in South Asia, primarily in Bangladesh and India, where the Ganges and Brahmaputra rivers meet and empty into the Bay of Bengal. This expansive delta is renowned for its rich biodiversity, fertile plains, and crucial role in supporting millions of people through agriculture and fisheries.
Q7. Which is the second largest river delta in India?
The second largest river delta in India is the Godavari Delta, located in the state of Andhra Pradesh. Formed by the Godavari River as it empties into the Bay of Bengal, this delta is known for its fertile plains and diverse ecosystems, supporting agriculture, fisheries, and wildlife.
Q8. What are the 5 sentences about the Sundarbans delta?
1. The Sundarbans Delta, located at the mouth of the Ganges, Brahmaputra, and Meghna rivers, is the largest in the world.
2. This sprawling mangrove forest delta spans an area of approximately 10,000 square kilometres, encompassing both Bangladesh and the Indian state of West Bengal.
3. Renowned for its dense mangrove forests and rich biodiversity, the Sundarbans Delta is a UNESCO World Heritage Site and a crucial habitat for numerous endangered species, including the Royal Bengal Tiger.
4. The delta plays a vital role in protecting coastal areas from cyclones and tidal surges, serving as a natural barrier against erosion and flooding.
5. In addition to its ecological significance, the Sundarbans Delta supports a significant human population engaged in fishing, agriculture, and other livelihood activities, highlighting the intricate relationship between humans and the natural world.
Q9. Why it is called the Sundarbans Delta?
The Sundarbans Delta is called so because it derives its name from the Sundari tree (Heritiera fomes), which is native to the region and is one of the dominant tree species found in the delta's mangrove forests. The term "Sundarbans" is a combination of two words: "Sundari," referring to the Sundari tree, and "ban," which means forest in Bengali. Therefore, "Sundarbans" translates to "beautiful forest," highlighting the lush and diverse mangrove forests that characterize this unique ecosystem. The abundance of Sundari trees in the delta's landscape has lent its name to the entire region, emphasizing its natural beauty and ecological significance.
Q10. What is Sundarban Delta for UPSC?
For the Union Public Service Commission (UPSC) examinations, the Sundarban Delta holds relevance primarily in the context of geography, environment, and biodiversity. UPSC aspirants may be required to have a comprehensive understanding of the Sundarban Delta's geographical location, formation, ecological significance, and conservation efforts. Additionally, knowledge about the delta's role in coastal protection, its impact on local communities, and relevant government policies and initiatives may also be pertinent for UPSC examinations, particularly in the General Studies paper. Therefore, candidates should familiarize themselves with various aspects of the Sundarban Delta, including its ecological importance, biodiversity, challenges, and conservation measures, to adequately prepare for UPSC exams.
Q11. What is the shape of the Sundarban delta?
The shape of the Sundarban Delta is predominantly triangular, owing to its formation at the confluence of the Ganges, Brahmaputra, and Meghna rivers. This triangular shape is characteristic of river deltas, where sediment carried by rivers is deposited at their mouths, gradually building up landmasses in a triangular pattern. However, the exact shape of the Sundarban Delta may vary due to factors such as tidal currents, sedimentation rates, and ongoing geological processes. Overall, the Sundarban Delta's triangular shape is a defining feature of its geographical landscape.
Q12. How does the Sundarban Delta look?
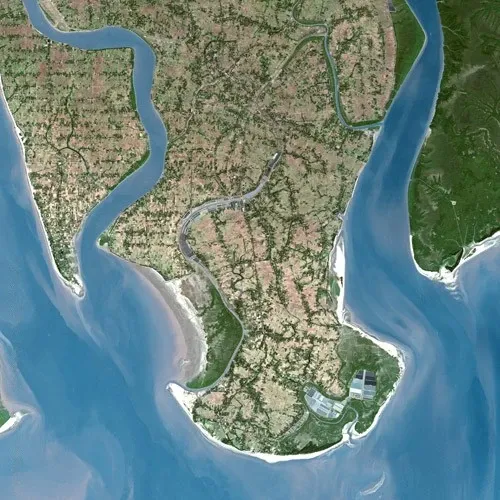
The Sundarban Delta is characterized by its stunning natural beauty, with a diverse array of landscapes and ecosystems. From aerial perspectives, it appears as a vast expanse of greenery, interspersed with intricate networks of waterways, creeks, and estuaries. The delta's coastline is lined with dense mangrove forests, which extend inland to form a dense canopy of trees. These mangroves are punctuated by tidal mudflats, salt marshes, and patches of open water, creating a mosaic of habitats that support a rich variety of flora and fauna. The Sundarban Delta's ever-changing landscape, shaped by the ebb and flow of tides and the movement of sediment, presents a dynamic and visually captivating spectacle that is both awe-inspiring and humbling.












আজকের আইটির নীতিমালা মেনে কমেন্ট করুন। প্রতিটি কমেন্ট রিভিউ করা হয়।
comment url